.png)
You may have been hearing about ‘HTTPS’ and what it means for the security of your website. We know that all websites are prefaced with an HTTP, but to really understand the switch to HTTPS, we need to start with the basics. What is HTTP? What is HTTPS? And why do we need to switch?
Let’s start from the beginning..
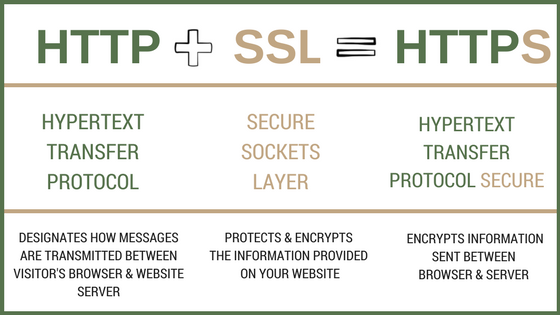
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. This is how a server sends or connects, the webpage you browse on to the server, and how the browser responds. On the major web browsers (Google, Firefox, Internet Explorer) you will see a green padlock next to the URL, indicating the site is secure.

What is HTTPS?
When you add an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) to HTTP, you get HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure). This refers to a technology that encrypts your connection to a website, so hackers or anyone else, can’t intercept any of your personal data.
Why Does HTTPS Matter? (Hint: It will improve your SEO)
When a user submits their data to a site with HTTPS, several things happen behind the scenes - the data becomes encrypted, rendering it useless for anyone trying to intercept the data, the data becomes impermeable to corruption, and finally, the data has a secure authentication, which prevents outside parties from tricking your customers into believing they’ve sent their data to you, when in fact they’ve sent it to a scammer.
In 2014, Google announced that every website should transfer over to HTTPS, and incentivized webmasters by giving HTTPS websites a higher search ranking over websites that had not completed the switch.
While it is essential for anyone who receives credit card information from their customers, it is quickly becoming known as a best practice for both user experience, and good common sense.
Plus, why not improve your SEO and give yourself an edge over your competitors that don't have HTTPS set up yet!
How Does HTTPS Work?
When a user submits their data on a site with HTTPS, several things happen behind the scenes - the data becomes encrypted, rendering it useless for anyone trying to intercept the data, the data becomes impermeable to corruption, and finally, the data has a secure authentication, which prevents outside parties from tricking your customers into believing they’ve sent their data to you, when in fact they’ve sent it to a scammer.
What’s the Process?
-
Obtain a web server that supports SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption.
-
Obtain a unique IP address for each domain that will have HTTPS.
-
Obtain an SSL certificate from a certified provider.
As you can tell, this stuff is pretty tricky to figure out if you’re not a tech guru. Have questions? Want help? If you want to switch your website over to a secured site, give us a call, we can help.



